
For example, the fields in one record of the Customers table together store all the information about one customer.įor the same reason, you should assign each customer a unique, identifying number.
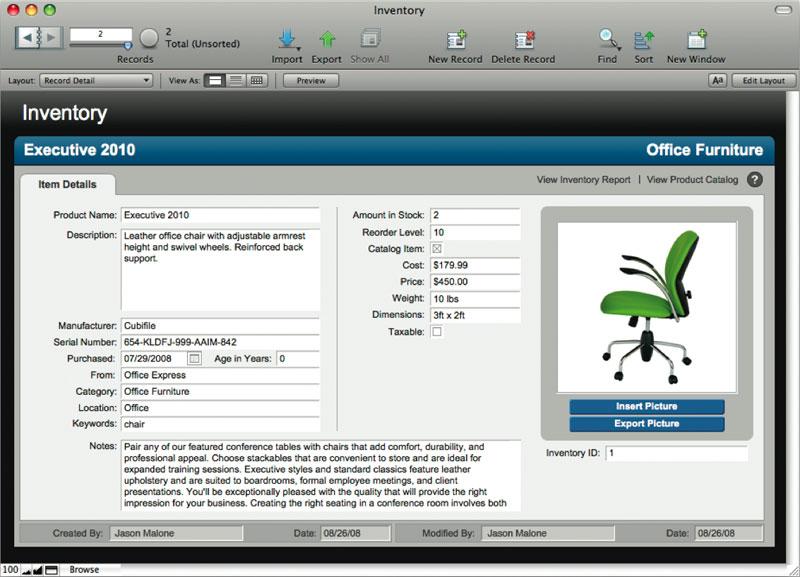
Determine the fields each table will need.Įach table has only one subject, and all fields in a table describe only that subject.a product may appear on many line items.To solve the problem in this example, add the intermediate table Line Items to store information about products sold.Īfter resolving the many-to-many relationship, this example shows:

You must resolve the many-to-many relationship by using an intermediate table, which breaks the many-to-many relationship into two one-to-many relationships. Relational databases handle one-to-one and one-to-many relationships directly. You cannot set up a many-to-many relationship directly between two tables.
If a table has no relationship to another, it’s probably unnecessary. For example, customers can have invoices and invoices can have products. Connect one table to another to indicate a relationship between them.You can do this by writing simple sentences that describe how the categories interact, such as "customers order products" and "invoices track customers’ orders." Determine how the tables are related to each other.
These categories will be tables in FileMaker Pro.įor example, a Sales database might include these tables: Customers, which includes customer information Invoices, which includes order information and Products, which includes product information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
